问题陈述:
给定一棵二叉树,实现中序遍历并返回包含其中序序列的数组。
例如给定下列二叉树:
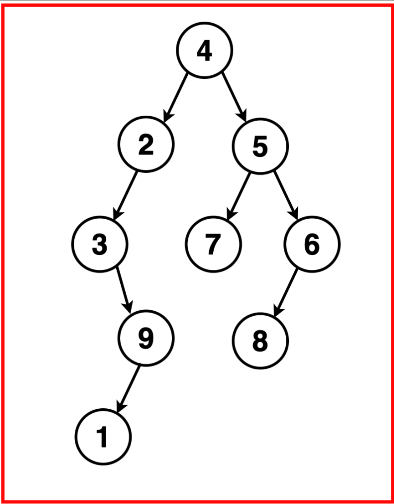
我们按照左、根、右的顺序递归遍历二叉树,得到以下遍历:
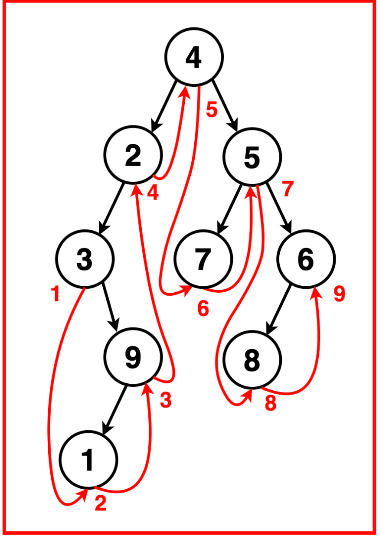
最终中序遍历结果可以输出为: [3, 1, 9, 2, 4, 7, 5, 8, 6]
Morris trick
Morris 中序遍历是一种树遍历算法,旨在实现 O(1) 的空间复杂度,无需递归或外部数据结构。该算法应高效地按中序顺序访问二叉树中的每个节点,并在遍历过程中打印或处理节点值,而无需使用堆栈或递归。关键思想是在 current node 与其对应的 rightmost node 之间建立临时链接
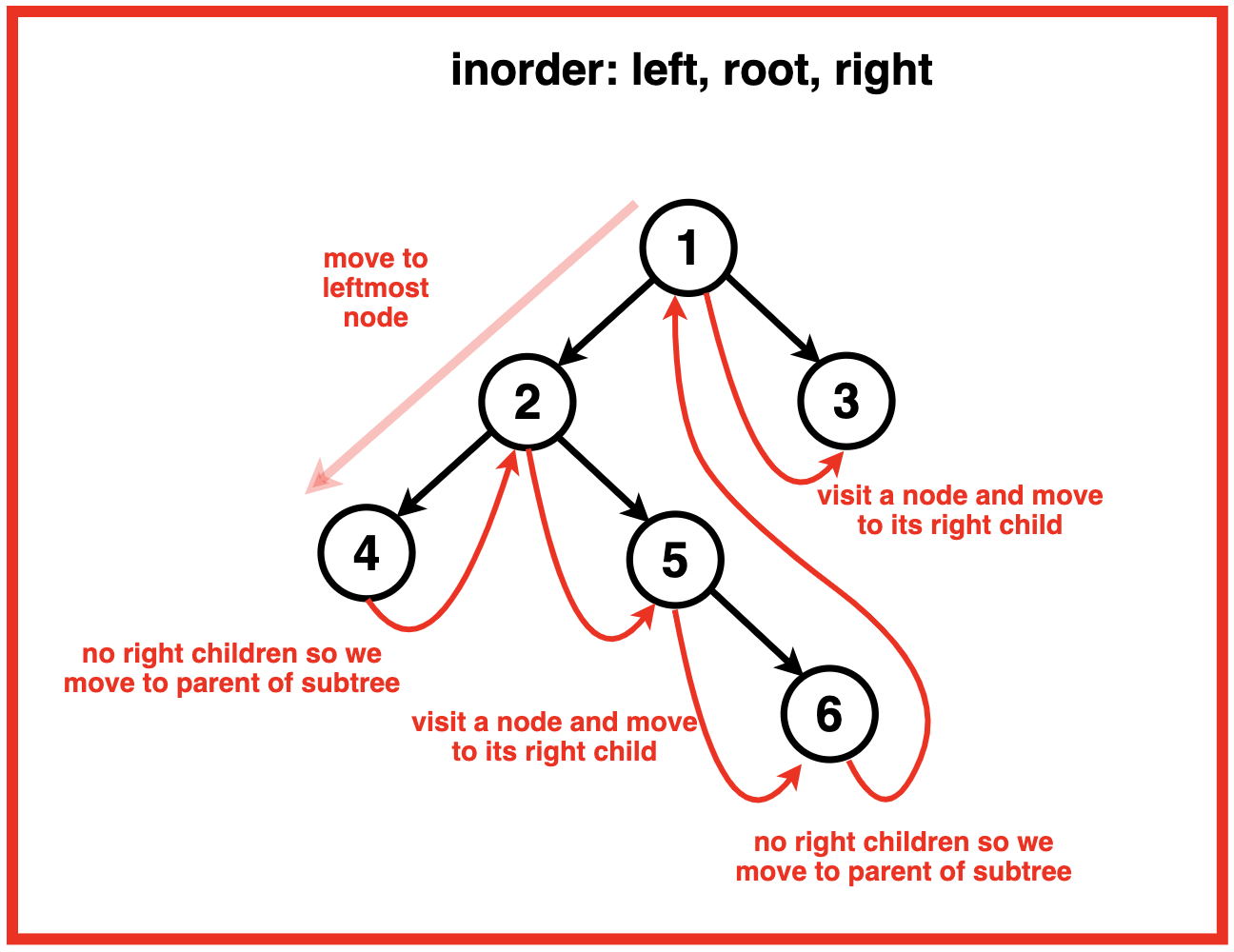
先来看下中序遍历的过程:
做法讨论
节点的中序前驱是左子树中最右边的节点。因此,当我们遍历左子树时,我们会遇到一个右子节点为空的节点,这是该子树中的最后一个节点。 因此,我们观察到一种模式,每当我们处于子树的最后一个节点时,如果右子节点指向空,我们就会移动到该子树的父节点。
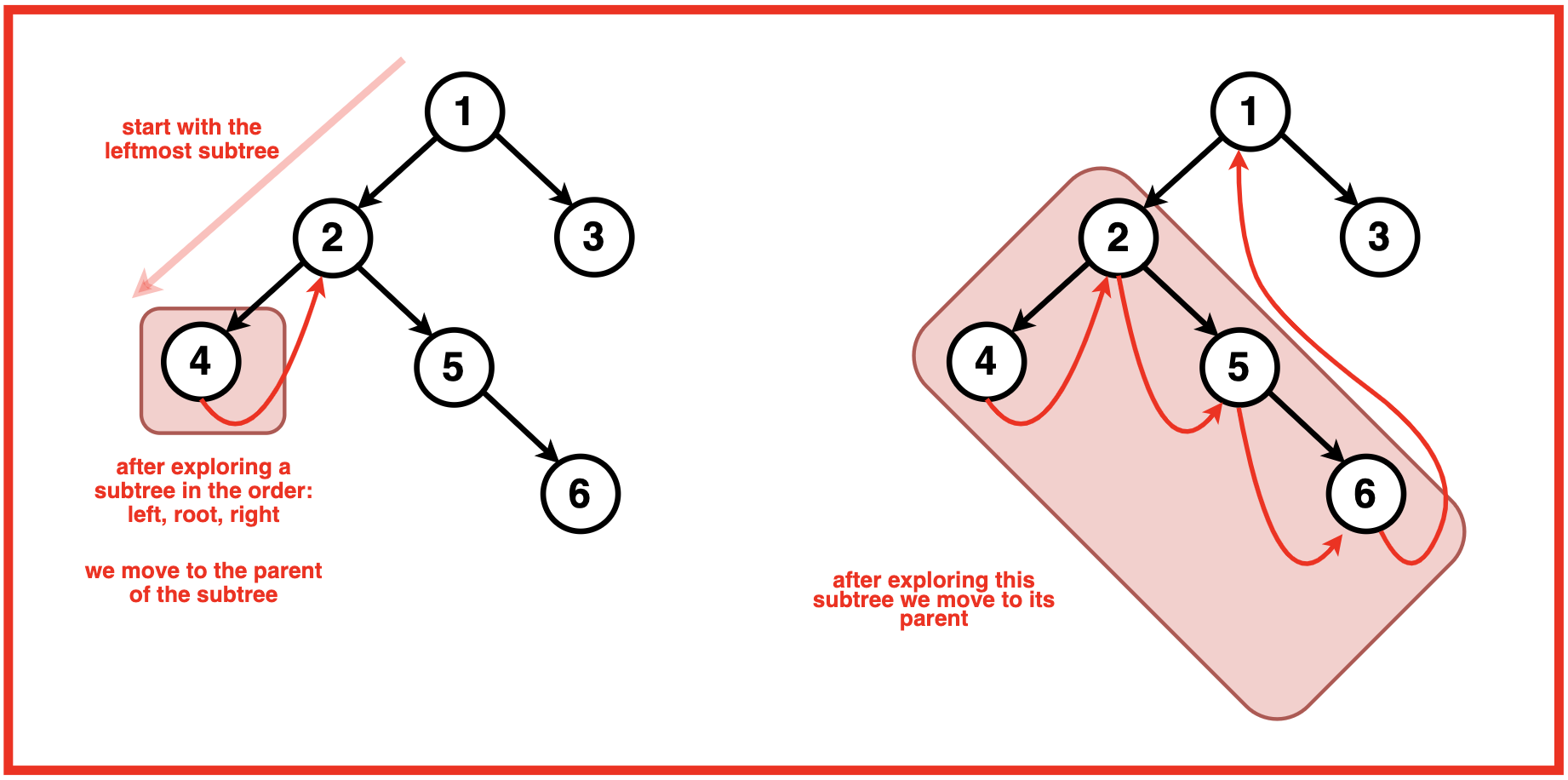
当我们当前处于某个节点时,可能会出现以下情况:
情况1:当前节点没有左子树
- 打印当前节点的值
-
然后到当前节点的右子节点
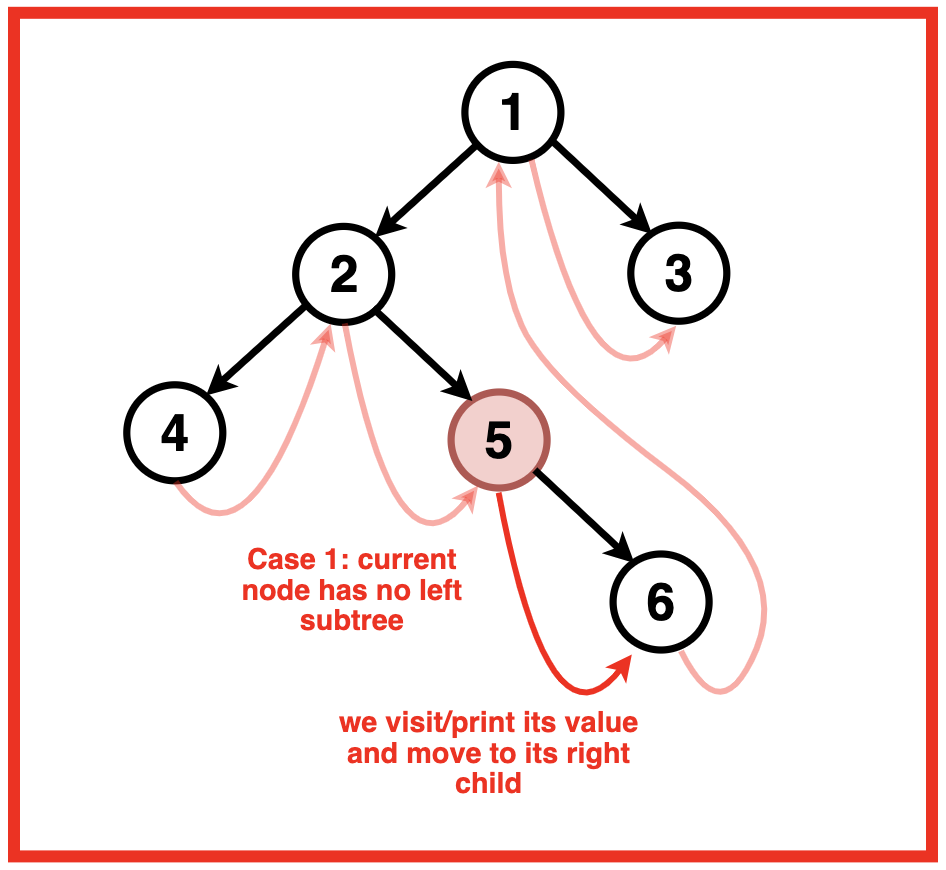
如果没有左子树,我们只需打印当前节点的值,因为左侧没有节点可遍历。之后,我们移至右子节点继续遍历。
情况 2:存在一棵左子树,并且该左子树的最右边的孩子指向空。
- 将左子树的最右边的子节点设置为指向当前节点。
-
移动到当前节点的左子节点。
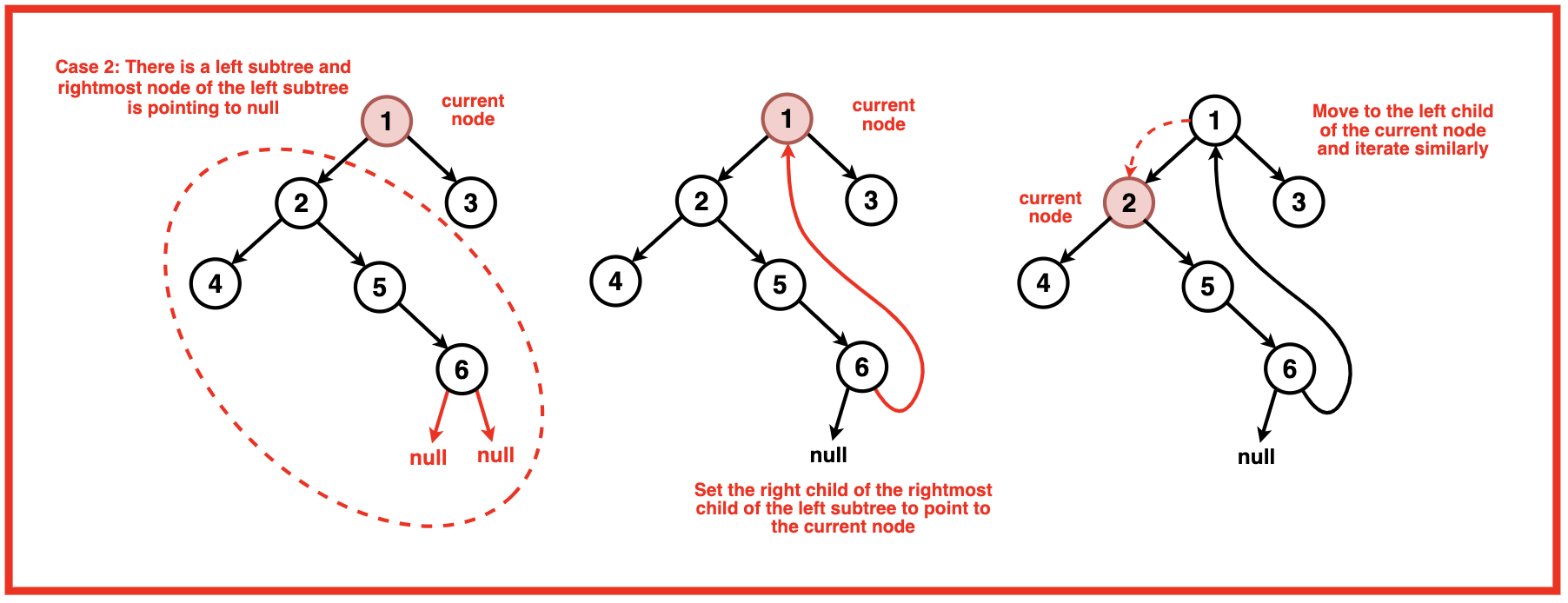
在这种情况下,我们还没有访问左子树。我们从左子树的最右节点到当前节点建立一个临时链接。 此链接可帮助我们稍后确定何时完成左子树的按序遍历 。设置链接后,我们移至左子节点以探索左子树。
情况3:存在一棵左子树,并且该左子树的最右边的孩子已经指向当前节点。
- 打印当前节点的值
- 恢复临时链接(将其设置回空)
-
移动到当前节点的右子节点
.
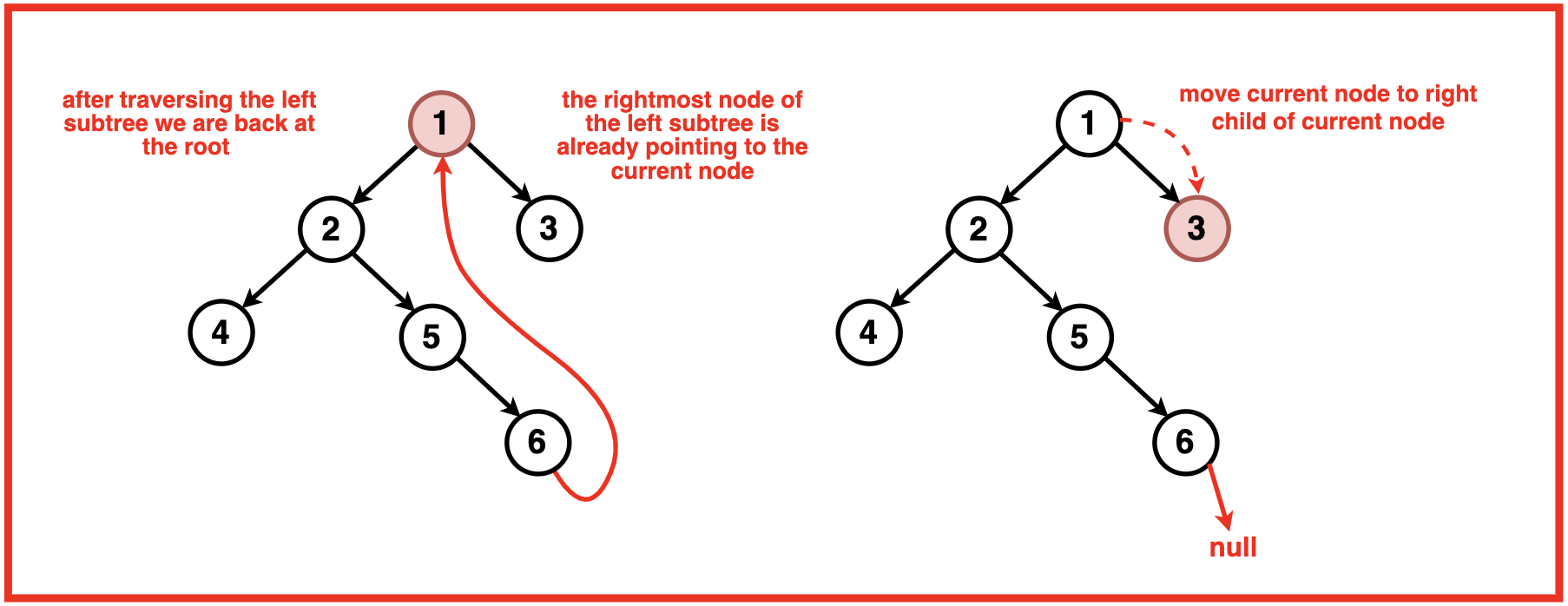
这种情况对于保持树结构的完整性至关重要。如果左子树的最右边的子节点已经指向当前节点,则意味着我们已经完成了左子树的按序遍历。我们打印当前节点的值,然后恢复临时链接以恢复原始树结构。最后,我们移动到右子节点继续遍历。
算法
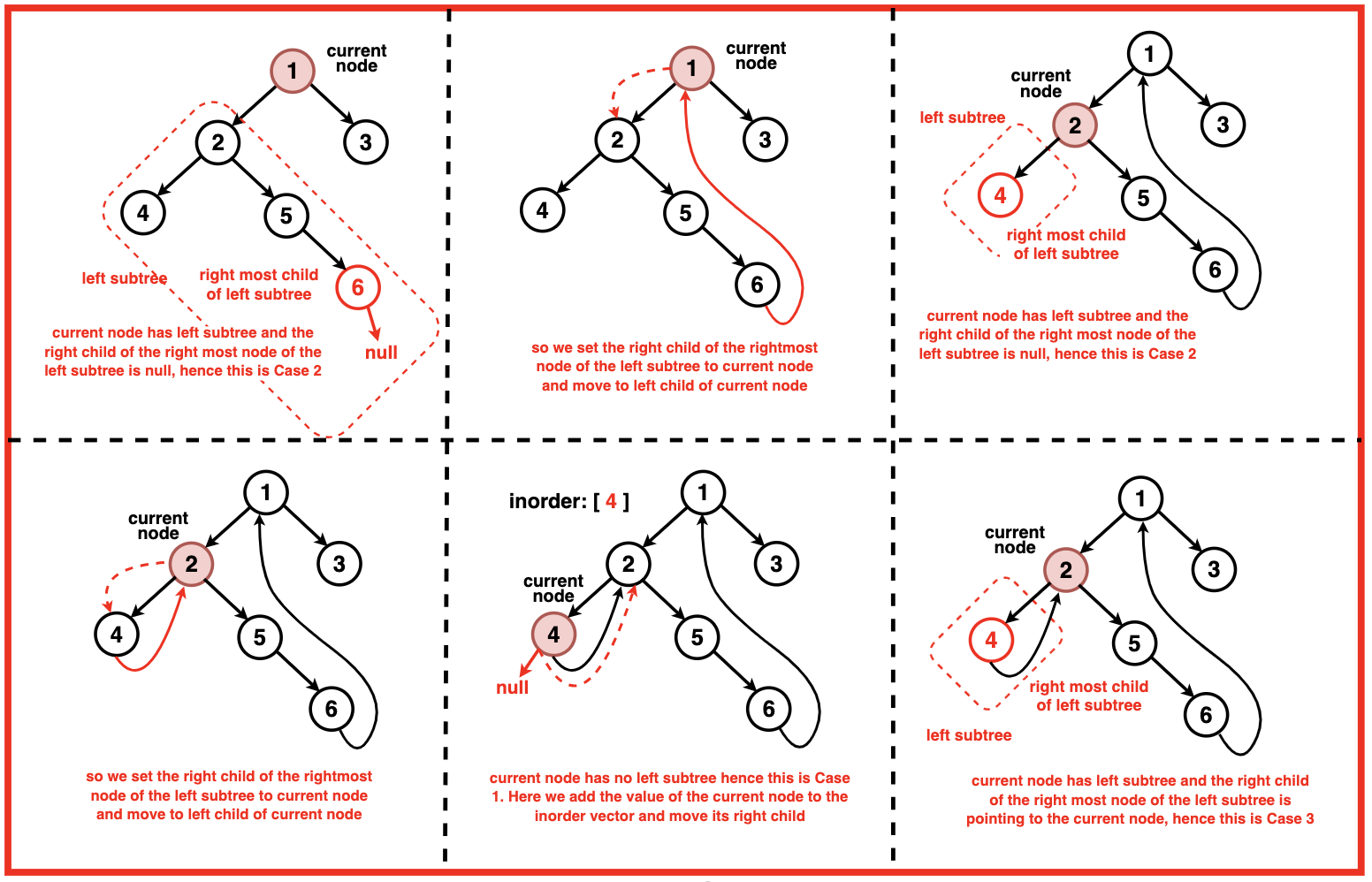
步骤 1:初始化 current 来遍历树。将 current 设置为二叉树的根。
步骤 2:当前节点不为空时:如果当前节点没有左子节点,则打印当前节点的值并移动到右子节点,即将当前节点设置为其右子节点。
步骤 3: 当前节点有左孩子,我们找到当前节点的 in-order predecessor 。这个 in-order predecessor 是左子树的最右节点。
-
如果 in-order predecessor 的右孩子节点为空:
- 将 in-order predecessor 右孩子节点设置为当前节点。
- 移动到 current 的左孩子
-
如果 in-order predecessor 的右孩子不为空:
- 通过in-order predecessor 的右孩子设置为空
- 打印当前节点的值。
-
通过先前 in-order predecessor 的右孩子拿到 current , 然后移动到 cuurent 的右孩子节点
重复步骤 2 和 3,直到到达树的末尾。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
// TreeNode structure
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// Function to perform iterative Morris
// inorder traversal of a binary tree
vector<int> getInorder(TreeNode* root) {
// Vector to store the
// inorder traversal result
vector<int> inorder;
// Pointer to the current node,
// starting from the root
TreeNode* cur = root;
// Loop until the current
// node is not NULL
while (cur != NULL) {
// If the current node's
// left child is NULL
if (cur->left == NULL) {
// Add the value of the current
// node to the inorder vector
inorder.push_back(cur->val);
// Move to the right child
cur = cur->right;
} else {
// If the left child is not NULL,
// find the predecessor (rightmost node
// in the left subtree)
TreeNode* prev = cur->left;
while (prev->right && prev->right != cur) {
prev = prev->right;
}
// If the predecessor's right child
// is NULL, establish a temporary link
// and move to the left child
if (prev->right == NULL) {
prev->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
} else {
// If the predecessor's right child
// is already linked, remove the link,
// add current node to inorder vector,
// and move to the right child
prev->right = NULL;
inorder.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
// Return the inorder
// traversal result
return inorder;
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
root->left->right->right = new TreeNode(6);
Solution sol;
vector<int> inorder = sol.getInorder(root);
cout << "Binary Tree Morris Inorder Traversal: ";
for(int i = 0; i< inorder.size(); i++){
cout << inorder[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
标签:游戏攻略








